-
[JS] Asynchronous JavaScript (callback,promise,async,await)공부 1/JS 2020. 11. 9. 11:08더보기
목표
- 어떤 경우에 중첩된 callback이 발생하는지 이해할 수 있다.
- 중첩된 callback의 단점, Promise 의 장점을 이해할 수 있다.
- Promise 사용 패턴과 언어적인 특징들을 이해할 수 있다.
- resolve, reject의 의미와, then, catch와의 관계를 이해할 수 있다.
- Promise 에서 인자를 넘기는 방법에 대해 이해할 수 있다.
- Promise의 세가지 상태를 이해할 수 있다.
- Promise.all 의 사용법을 이해할 수 있다.
- async/await keyword에 대해 이해하고, 작동 원리를 이해할 수 있다.
- node.js의 fs 모듈의 사용법을 이해한다.
클라이언트 - 서버로 접속하는 컴퓨터
서버 - 무언가(서비스, 리소스 등)를 제공하는 컴퓨터
synchronous - 클라이언트에서 요청을 받아 서버에 전달하면 서버에서 리스폰이 올 때까지 암것도 안하고 기다림
asynchronous - 클라이언트에서 요청을 받아 서버에 전달하고, 서버에서 처리가 이루어 지는동안 새로운 요청받기 등 일을 계속 함
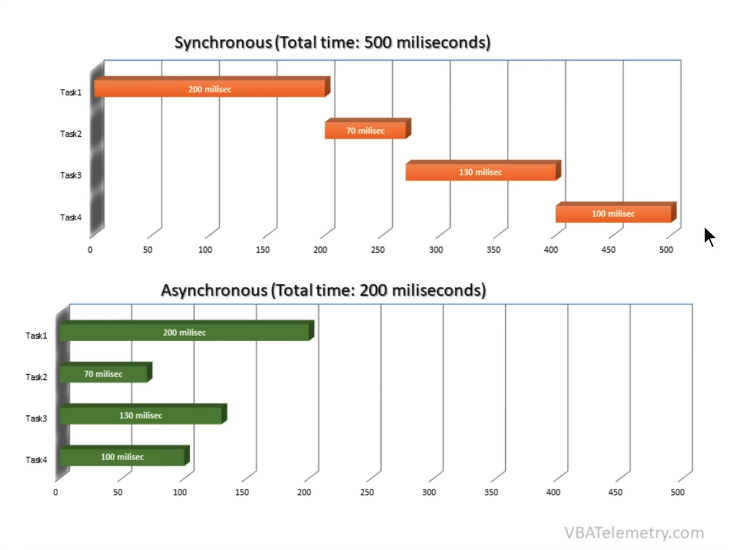
Async는 효율적이라는 장점을 가진 반면에 동시다발적으로 실행하면 결과의 순서를 예상할 수 없다.
Async의 순서를 제어하는 방법에는 3가지가 있다.
0. 병렬적으로 실행한 Async
const printString = (string) =>{ setTimeout( ()=>{ console.log(string) }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1 ) } const pringAll = () => { printString("A") printString("B") printString("C") } printAll() // A B C 무작위로 출력1. callback 함수 사용
callback함수를 통해 순서를 지정해줄 수 있다.
const printString = (string, callback) =>{ setTimeout( ()=>{ console.log(string) callback() }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1 ) } const pringAll = () => { printString("A", () => { pringString("B", () => { printString("C", () => {}) }) }) } printAll() // A B C 순서대로 출력이렇게 콜백함수도 파라미터로 받는 printString함수를 만들고 콜백함수로 다음 함수를 넣으면된다.
순서를 정할 수 있지만 들여쓰기의 늪에 빠진다는 함정이 있다. 나는 분명 잘 작성했는데 티스토리 코드블럭 너무 구리다 ;;
2. promise 사용
const printString = (string, callback) => { setTimeout( () => { console.log(string) callback() }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1 ) } const printAll = () => { printString("A") .then(() => { return printString("B") }) .then(() => { return printString("C") }) } printAll() //ABC 순서대로 출력promise는 되게 쉬운듯 하면서 어렵다.. 따로 다뤄봐야할듯
3.async / await 사용
function gotoCodestates() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1) }) } function sitAndCode() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1) }) } function eatLunch() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1) }) } function goToBed() { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. goToBed') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1) }) } const result = async () => { const one = await gotoCodestates(); console.log(one) const two = await sitAndCode(); console.log(two) const three = await eatLunch(); console.log(three) const four = await goToBed(); console.log(four) } result();await은 async안에서만 쓸 수 있는데, 뒤에는 프로미스 함수만 들어갈 수 있다.
의미는 그 프로미스 함수가 끝날 때까지 기다린다는 뜻........................................................................................................
'공부 1 > JS' 카테고리의 다른 글
객체지향 자바스크립트 (OOP) (0) 2021.02.27 [JS] module(commonJS, import export) (0) 2020.12.18 [JS] 호이스팅, 함수선언식, 함수표현식 (0) 2020.10.31 [JS] Object.create 메소드 (0) 2020.10.28 [JS] Math 메소드 (0) 2020.10.22